Ceftin (cefuroxime) is a common antibiotic for sinus, ear, and lung infections. Learn how it compares to amoxicillin, cephalexin, azithromycin, and others in effectiveness, safety, cost, and side effects.
If you've ever been prescribed antibiotics, cefuroxime might sound familiar. It’s an antibiotic used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, from respiratory problems to skin infections. Many people wonder how it works and what they should watch out for when taking it. This guide breaks down the essentials so you can feel confident about your treatment.
Cefuroxime belongs to a group called cephalosporin antibiotics. It fights bacteria by stopping their cell wall growth, which basically kills them or stops them from multiplying. Doctors often recommend it for infections like bronchitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and certain skin infections. It’s a go-to choice when penicillin can’t be used or when infections need a stronger antibiotic.
Taking cefuroxime exactly as prescribed is crucial. Skipping doses or stopping early can lead to resistant bacteria that are harder to treat. Some people might experience side effects like stomach upset or mild diarrhea, but most tolerate it well. A key point is to watch for any allergic reactions, especially if you have a history of allergies to penicillin or other antibiotics. If you start feeling itchy, swollen, or have trouble breathing, seek medical help immediately.
Also, keep in mind that antibiotics like cefuroxime don't work against viruses, so they won’t help with the flu or common colds. Taking antibiotics unnecessarily can cause more harm than good by impacting gut bacteria or causing resistance problems down the line.
In a nutshell, cefuroxime is a valuable medication when used right. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions, report any side effects, and never share your medication with others. With proper use, it can be the medicine you need to get back on your feet quickly.

Ceftin (cefuroxime) is a common antibiotic for sinus, ear, and lung infections. Learn how it compares to amoxicillin, cephalexin, azithromycin, and others in effectiveness, safety, cost, and side effects.
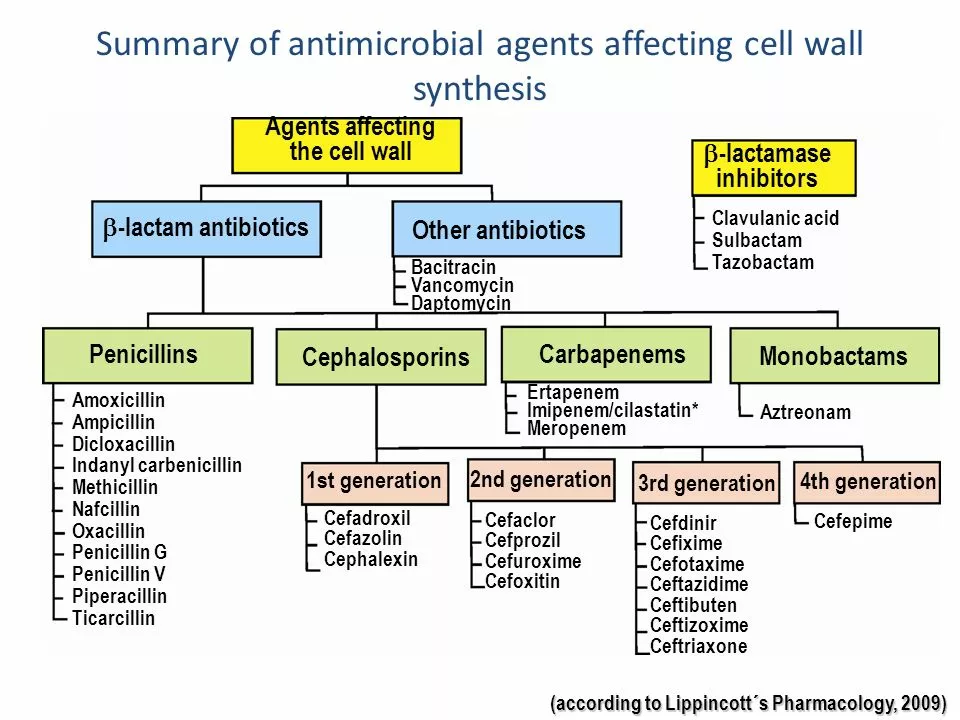
In my latest blog post, I delved into a comparative analysis between Cefuroxime and other antibiotics. I discovered that while Cefuroxime is effective in treating a wide range of bacterial infections, it may not always be the best choice depending on the specific condition being treated. I also explored how other antibiotics, such as penicillin and tetracyclines, might be more appropriate in certain cases. Moreover, I discussed the importance of considering factors like side effects, drug interactions, and individual patient needs when determining the most suitable antibiotic. Overall, my analysis emphasized the significance of tailored treatment approaches in optimizing patient outcomes.