A detailed 2025 guide comparing Xenical (Orlistat) with other weight‑loss meds, covering mechanisms, costs, side‑effects, and how to choose the right option.
When talking about Weight loss pills, oral products designed to help people reduce body weight by affecting appetite, metabolism, or fat absorption. Also known as diet pills or slimming pills, they range from prescription drugs to over‑the‑counter supplements. A common subset is appetite suppressants, ingredients that curb hunger signals in the brain (often called satiety agents), which many people rely on to cut calories without feeling deprived. Understanding how these components interact helps you decide if a pill fits your health goals.
Weight loss pills encompass several categories, each with its own rules and risks. Prescription weight loss medications, FDA‑approved drugs such as phentermine, liraglutide, or bupropion/naltrexone that require a doctor’s order (also called medical‑grade diet pills), are backed by clinical trials showing modest weight reductions when paired with diet and exercise. In contrast, over‑the‑counter diet pills, store‑bought products that often contain herbal extracts, caffeine, or thermogenic agents (sometimes labeled as fat burners) are marketed without prescription but still fall under regulatory scrutiny for safety claims. The central topic, weight loss pills, requires professional guidance because effectiveness depends on dosage, individual metabolism, and existing health conditions. Moreover, side effects such as increased heart rate, insomnia, or nutrient deficiencies can arise, especially when pills are used without a balanced diet and regular activity. Combining a pill with lifestyle changes creates a synergistic effect, turning a short‑term aid into a sustainable habit.
Beyond the drug class itself, you should weigh the role of metabolism boosters, nutrient interactions, and long‑term health outcomes. Fat burners, a sub‑type of weight loss pills, aim to raise basal metabolic rate through ingredients like green tea extract or yohimbine, but research shows mixed results and potential overstimulation. Likewise, appetite suppressants influence hormone pathways (for example, leptin and ghrelin), meaning they can interfere with natural hunger cues if misused. Knowing that weight loss pills influence both physiological and psychological factors lets you set realistic expectations and avoid common pitfalls like rapid weight regain after stopping the medication. Weight loss pills are most beneficial when they complement a personalized plan that includes nutrition counseling, regular exercise, and regular medical monitoring. Below you’ll find a curated collection of articles that dive deeper into specific drugs, safety tips, and evidence‑based strategies to help you navigate the complex world of weight management safely and effectively.
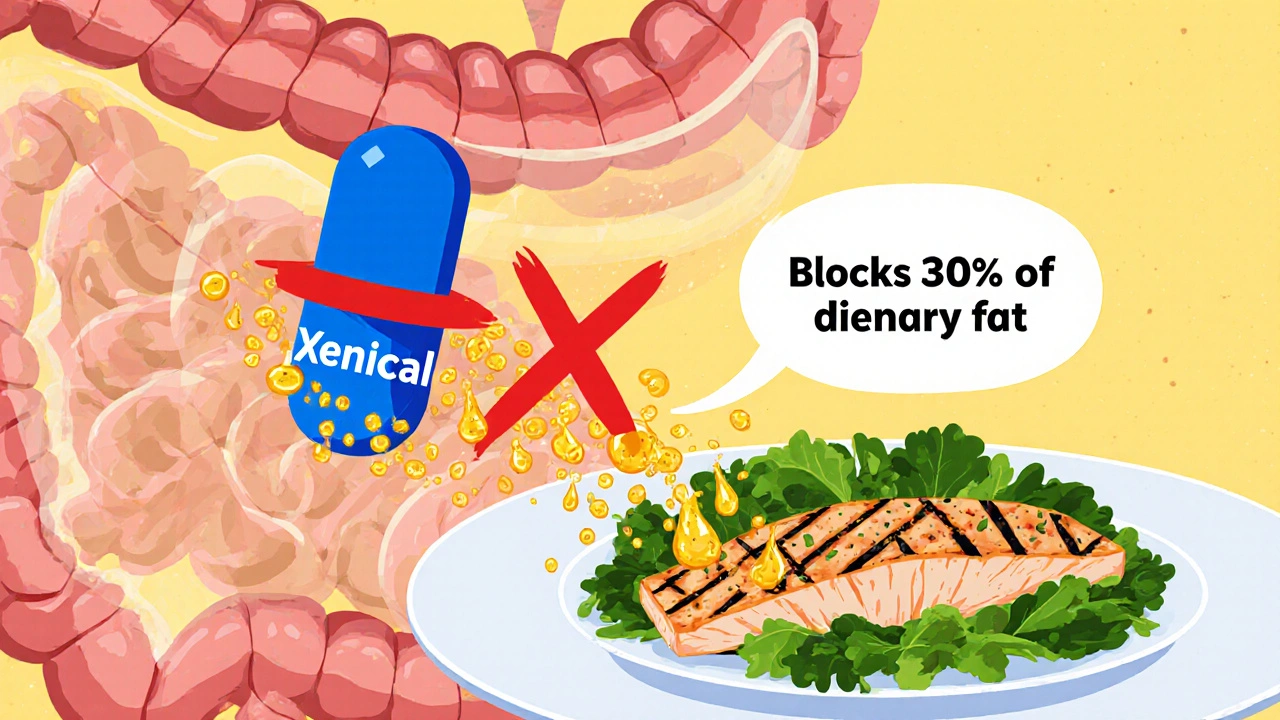
A detailed 2025 guide comparing Xenical (Orlistat) with other weight‑loss meds, covering mechanisms, costs, side‑effects, and how to choose the right option.