Learn how to choose between acetaminophen and NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen for OTC pain relief. Understand which works best for headaches, arthritis, or fever-and how to avoid serious side effects.
When you have a headache, sore back, or achy joints, OTC pain medication, over-the-counter drugs used to relieve mild to moderate pain without a prescription. Also known as non-prescription pain relievers, these are the first line of defense for millions of people—but they’re not harmless. Many assume that because they’re sold next to candy and gum, they’re safe to use anytime, anywhere. But that’s not true. OTC pain medication can damage your liver, kidneys, and stomach if used carelessly—even at recommended doses.
Two main types dominate the shelves: NSAIDs, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that reduce inflammation and pain. Also known as anti-inflammatories, they include ibuprofen and naproxen. And acetaminophen, a pain reliever and fever reducer that doesn’t reduce inflammation. Also known as paracetamol, it’s the active ingredient in Tylenol. NSAIDs work well for swelling and joint pain, but they raise your risk of stomach bleeding and high blood pressure. Acetaminophen is gentler on the stomach but is the #1 cause of acute liver failure in the U.S. when taken in excess—even just a few extra pills over a few days.
People often mix these without realizing it. Cold medicines, sleep aids, and even some migraine pills contain acetaminophen. Taking two different products at once can easily push you over the safe daily limit of 3,000 to 4,000 mg. Older adults, people with liver disease, or those who drink alcohol regularly are at higher risk—and they’re often the ones using these meds the most. And while NSAIDs help with arthritis pain, long-term use can silently damage your kidneys. You won’t feel it until it’s too late.
There’s no magic pill that fixes everything without side effects. But knowing what’s in your medicine cabinet—and how to use it wisely—can keep you out of the ER. The best OTC pain relief isn’t always the strongest. Sometimes it’s the most targeted. For a sprained ankle? Ibuprofen. For a tension headache? Acetaminophen. For chronic back pain? Maybe it’s time to talk to your doctor instead of reaching for another bottle.
What you’ll find here isn’t a list of brands. It’s a clear-eyed look at how these common drugs really work, who they help, who they hurt, and how to avoid the traps most people don’t even know exist. From hidden interactions with blood pressure meds to the quiet damage they do over time, these posts give you the facts you won’t get from a pharmacy shelf.
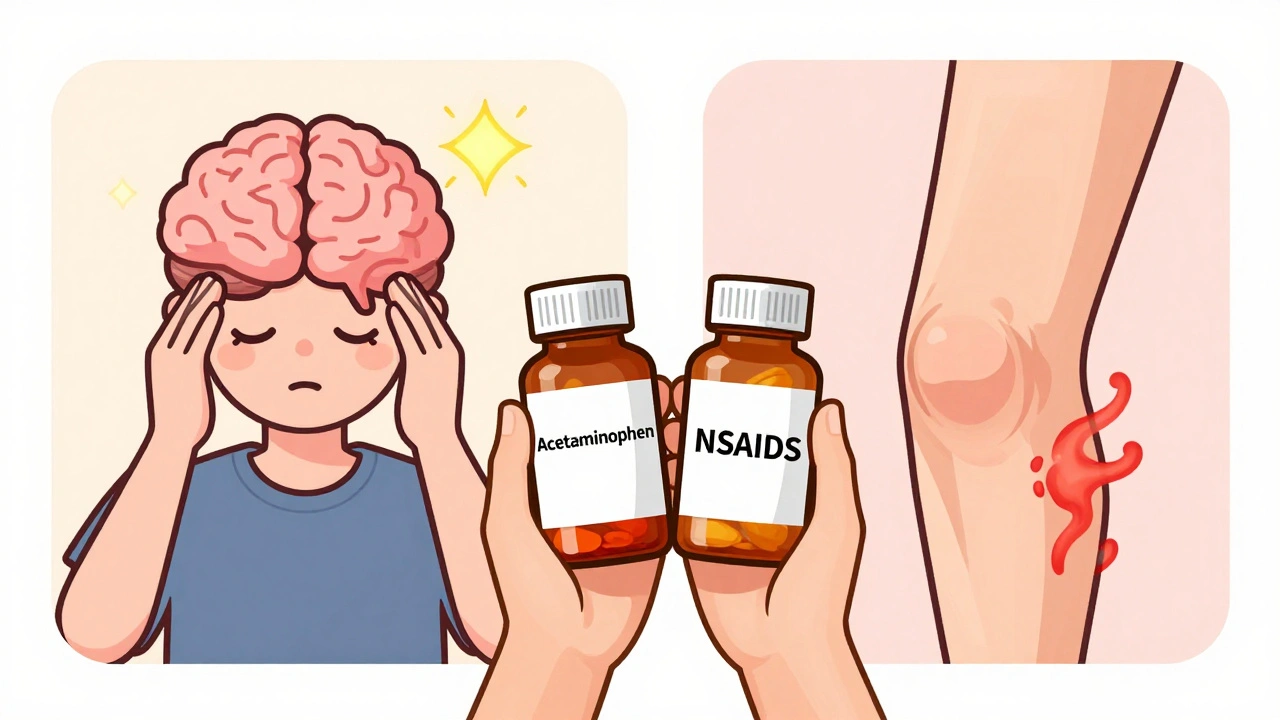
Learn how to choose between acetaminophen and NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen for OTC pain relief. Understand which works best for headaches, arthritis, or fever-and how to avoid serious side effects.