Understanding Dapagliflozin and its Role in Diabetes Management
Dapagliflozin is a medication commonly prescribed for patients with type 2 diabetes. It's a part of a class of drugs known as SGLT2 inhibitors, which work by helping the kidneys remove excess glucose from the bloodstream. By doing so, dapagliflozin helps lower blood sugar levels, thus providing better overall diabetes management.
In this article, we will explore the potential risks associated with dapagliflozin, particularly focusing on the risk of hypoglycemia. We will also discuss the precautions patients should take and how to recognize the warning signs of hypoglycemia.
Defining Hypoglycemia: Signs, Symptoms, and Complications
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, is a common concern for individuals with diabetes. It occurs when blood glucose levels drop below the normal range, usually below 70 mg/dL. Hypoglycemia can cause a variety of symptoms, including dizziness, confusion, trembling, sweating, rapid heartbeat, and even seizures or unconsciousness in severe cases.
If left untreated, hypoglycemia can lead to serious complications, such as brain damage, coma, and in extreme instances, death. Therefore, it's crucial for individuals with diabetes to be aware of the warning signs of hypoglycemia and know how to treat it promptly.
Assessing the Risk of Hypoglycemia with Dapagliflozin
While any diabetes medication can potentially cause hypoglycemia, the risk with dapagliflozin is considered to be relatively low. This is because SGLT2 inhibitors like dapagliflozin work independently of insulin, which means they are less likely to cause a sudden drop in blood sugar levels.
However, the risk of hypoglycemia may increase when dapagliflozin is used in combination with other diabetes medications, particularly insulin or sulfonylureas. Be sure to discuss your specific treatment plan and the potential risks of hypoglycemia with your healthcare provider.
Precautions to Minimize the Risk of Hypoglycemia
There are several steps you can take to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia while taking dapagliflozin or any other diabetes medication. These include:
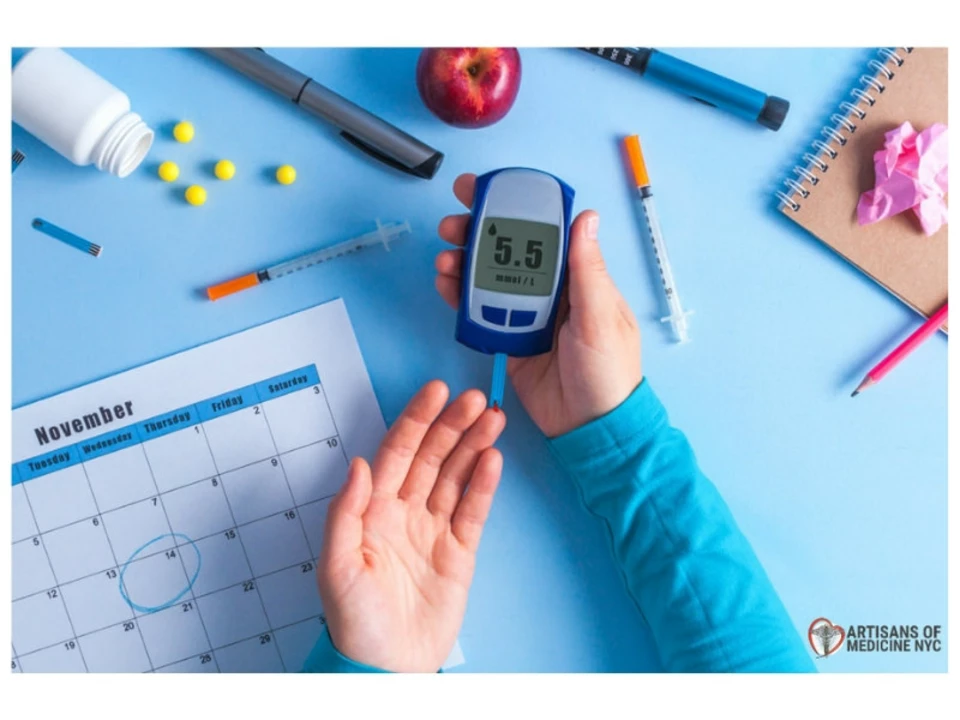
1. Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels, as recommended by your healthcare provider. This will help you identify any changes or trends that may indicate a need to adjust your medication or lifestyle.
2. Eating regular meals and snacks, and ensuring that your diet includes a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. This can help stabilize your blood sugar levels throughout the day.
3. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, as this can interfere with your body's ability to regulate blood sugar.
4. Being aware of the potential for hypoglycemia during periods of increased physical activity, and adjusting your food intake or medication as needed.
5. Working closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized diabetes management plan that takes into account your specific needs and risk factors.
Recognizing and Treating Hypoglycemia
If you suspect that you may be experiencing hypoglycemia, it's important to take action immediately. Check your blood sugar levels to confirm whether they are indeed low. If so, follow the "15-15 Rule": Consume 15 grams of a fast-acting carbohydrate (such as fruit juice, glucose gel, or hard candy), wait 15 minutes, and then re-test your blood sugar levels. If they remain low, repeat the process until your levels return to normal.
Remember to always carry a source of fast-acting carbohydrate with you, in case of a hypoglycemic episode. In addition, inform your friends, family, and coworkers about the signs of hypoglycemia and what to do if they suspect you are experiencing a low. This can help ensure that you receive prompt and appropriate treatment if needed.
When to Contact Your Healthcare Provider
While hypoglycemia can usually be treated quickly and effectively at home, it's essential to inform your healthcare provider if you experience frequent or severe episodes. They may need to adjust your medication or recommend additional lifestyle changes to help manage your blood sugar levels more effectively.
Additionally, if you experience any unusual or persistent side effects while taking dapagliflozin, such as increased thirst, frequent urination, or signs of a urinary tract or yeast infection, contact your healthcare provider for guidance.
Conclusion: Staying Informed and Proactive
While the risk of hypoglycemia with dapagliflozin is relatively low, it's crucial for individuals with diabetes to remain informed about the potential risks associated with their medications. By understanding the warning signs of hypoglycemia, taking precautions to minimize the risk, and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can help ensure that you maintain safe and effective blood sugar control while on dapagliflozin or any other diabetes medication.



Comments
When you start looking at how dapagliflozin works, the first thing that jumps out is its kidney‑targeted mechanism, which means it sidesteps the insulin pathway entirely. That alone drops the baseline risk of a sudden sugar plunge, especially compared to sulfonylureas. Still, the body isn’t a simple machine, and when you combine it with other glucose‑lowering agents, the dynamics shift. For anyone juggling insulin or a sulfonylurea, a slight dip in blood sugar can become noticeable, so tweaking doses becomes essential. Regular self‑monitoring is the golden rule; a quick finger prick before a meal can flag trends before they turn into emergencies. Pair that with consistent meal timing, and you give your pancreas a predictable environment to operate in. Hydration plays a hidden role too-staying well‑hydrated helps the kidneys flush glucose without over‑loading the system. And let’s not forget that alcohol can suppress gluconeogenesis, making the hypoglycemia risk creep up even if you’ve been diligent all day.
When an episode does strike, the 15‑15 rule is a lifesaver: 15 grams of fast‑acting carbs, wait 15 minutes, retest, and repeat if needed. Carrying glucose tablets or a small juice box can make that process painless and fast. Educating friends, coworkers, and family members about the signs-shakiness, sweating, confusion-creates a safety net that can be the difference between a quick fix and a hospital trip. If episodes become frequent, it’s a signal to your healthcare provider that your regimen may need fine‑tuning, whether that means adjusting dapagliflozin dose or re‑evaluating companion meds. Also watch out for side‑effects like increased thirst or urinary changes, which can hint at complications beyond just blood sugar swings.
Bottom line: dapagliflozin offers a low‑hypoglycemia profile when used wisely, but it’s not a free pass. Pair it with vigilant monitoring, balanced nutrition, and open communication with your care team, and you’ll maximize its benefits while keeping the low‑sugar scares at bay.
i cant help but think that every med is like a tiny philosopher, whispering its own truth to our bodies, sometimes we ignore the whisper and get a shout, lol typo's happen but the point stands
Dapagliflozin rarely causes low sugar unless mixed with insulin
Meh, another drug article.
I find the interplay between glucose excretion and insulin independence fascinating, and it really underscores why patient education is key.
Great rundown! Keep an eye on those carbs and stay proactive-your health will thank you.
Oh wow, because we all love counting carbs 🍽️🤦♂️.
Clinically, the risk profile aligns with the pharmacodynamics of SGLT2 inhibition, especially when not paired with insulin secretagogues.
You’ve nailed the key points, just remember to personalize adjustments based on activity level and diet.
When blood sugar drops, it feels like a roller‑coaster 🎢, stay prepared and have those fast carbs handy!
Looks fine.
Indeed, the synopsis captures the essentials with crisp clarity.
Watch out for that missing comma after “however” 👀!
It should be “When used in combination,” not “When used in combination”.
Simple advice, but effective.
Yo, this SGLT2 stuff is straight‑up game changer for the metabolic battlefield.
Love the detail, especially the 15‑15 rule 🙌.
Exactly, stay vigilant and tweak as needed.